DSRC vs. C-V2X
DSRC vs. C-V2X for Safety Applications
General
DSRC was the first V2X technology available. It is currently widely deployed on roads in Austria and Germany, with plans for expansion to other European states. Volkswagen incorporates DSRC in models such as Golf and the EV line-up sold in Europe.
C-V2X technology serves the same purpose of establishing a direct communication link between vehicles. C-V2X is defined by 3GPP based on cellular modem technology, leading to a fundamentally different non-interoperable access layer with DSRC. Aside from that, the two technologies address identical use-cases and have identical network, security, and application layers.
The first-generation C-V2X (Releases 14/15) is called LTE-V2X, and the second (Releases 16 and later) is called 5G-V2X. China is in the process of widespread LTE-V2X deployment. The FCC also selected LTE-V2X for mass deployment in the United States. 5G-V2X is expected to make its way into European vehicles in the future.
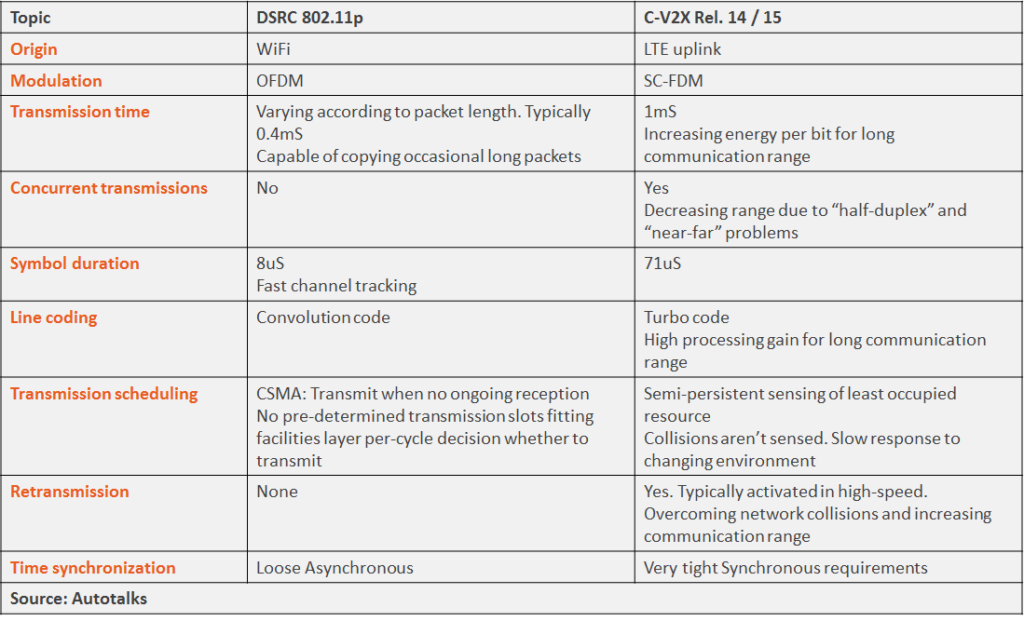
The table highlights the commonalities and differences between the usability and general properties of DSRC and C-V2X. A more detailed technical comparison, can be found in the “Technical” tab.
Technical
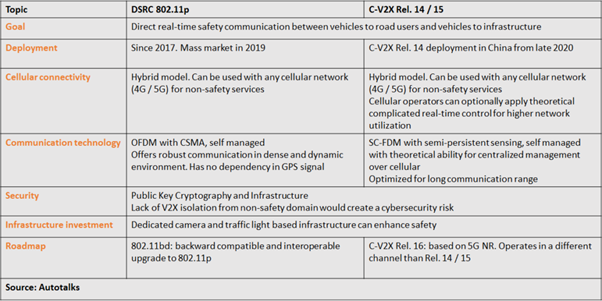
DSRC and C-V2X are rooted from different technologies, leading to fundamentally different operational methods. DSRC, derived from WiFi, is optimized for cost and simplicity, and inherently supports distributed operation. C-V2X, derived from LTE, added new mechanisms to enable distributed operation (mode 4).
The comparison is multi-dimensional. The impact of every parameter should be analyzed according to the properties of V2V operation, as defined by the requirements of the V2V upper-layers and applications.
The following table summarizes the technical properties of DSRC and C-V2X technologies: